Publication models
How data is brought on-chain through an Orcfax oracle feed depends largely on the use case and the needs of integrators and their dApps; there are many different oracle use cases, and each needs something different from Orcfax. While there can be overlap in the data needs of smart contracts, many of these use cases have their own distinct requirements regarding when data is needed. Because of the varied needs of our integrators, Orcfax is developing publication options that allow integrators to choose services that best meet their needs.
Orcfax feeds will now support two distinct publication models: our existing heartbeat model, and a new on-demand model.
By providing integrators the ability to choose the publication model, Orcfax will enable dApps to increase flexibility and cost efficiency by choosing how best to receive their data: hourly, daily or when there's a real-time requirement for the data.
The heartbeat publication model
The heartbeat publication model gives integrators the ability to access data at regular intervals which can be parameterized according to their needs (e.g. every 5 minutes, once per hour, etc.). This model can be further enhanced when paired with a monitoring feature which adds a deviation formula; heartbeat publication models with deviation add improved precision by guaranteeing data at both a consistent interval and when integrator-stipulated thresholds have been met (e.g. publish immediately before the next heartbeat if price changes by x%).
In the heartbeat publication model, nodes request and cache primary source data every minute. Publications are made at a fixed rate (in this case on the hour) that is set by the integrator, and additional publications can be triggered by utilizing the monitoring function in the event of deviations.
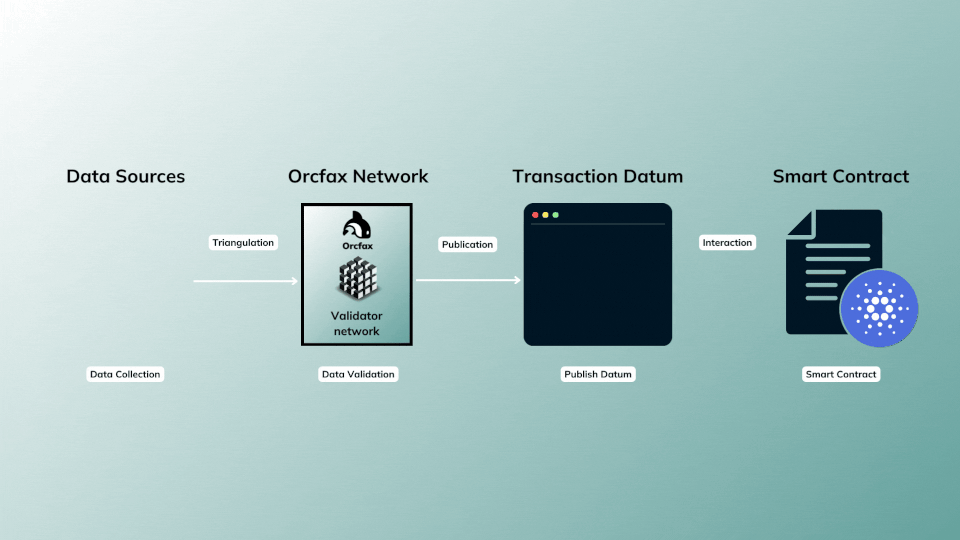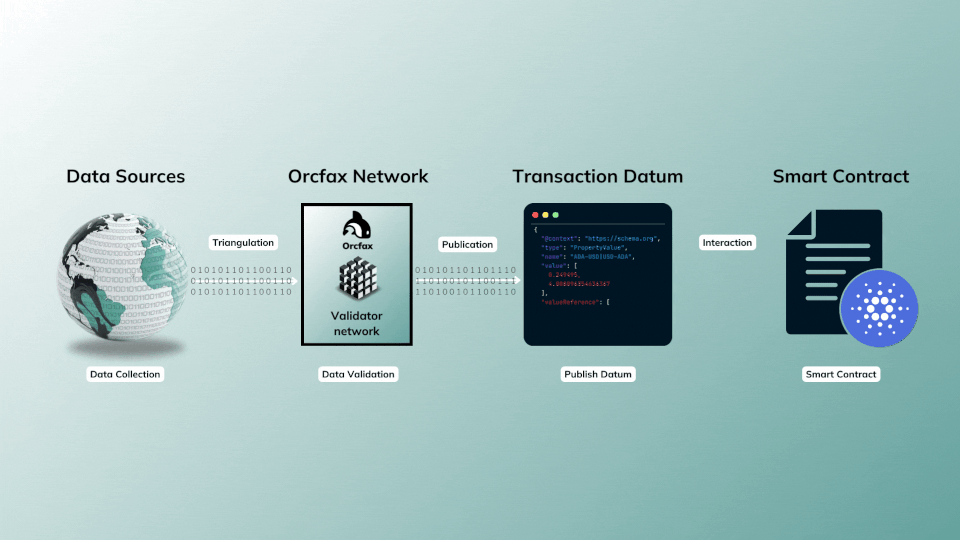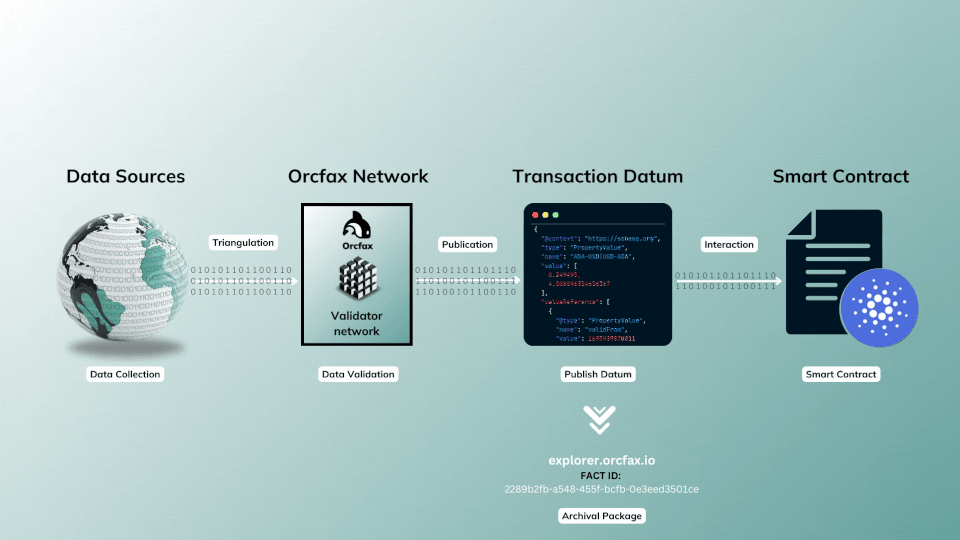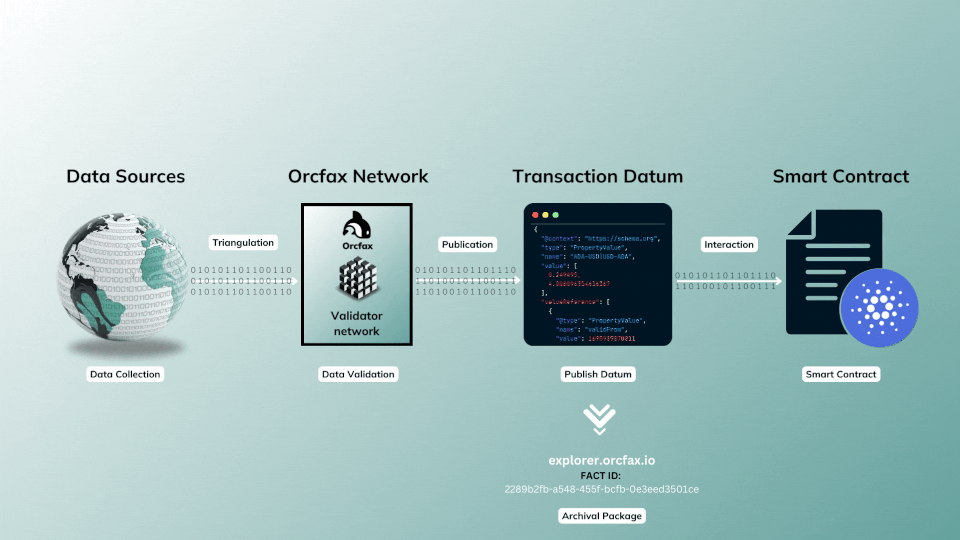
This publication model is often referred to as a push based oracle, as the oracle service is parameterized to publish (push) data, and does so continuously at predefined intervals so long as the feed remains funded.
The benefits of the heartbeat publication model is that integrators receive data continuously. However, if the dApp provides services which only need data inputs for specific actions, at unpredictable times, or to verify components of a transaction, then this model can be suboptimal or costly given the rate at which data is received versus instances of data use; this inefficiency for some of our integrator's use cases led us to begin development on the Orcfax on-demand model.
The on-demand publication model
The on-demand publication model allows complete flexibility and gives dApps even more control of data use by allowing them to request data collection, validation, and publication whenever it's needed by their smart contracts.
If an Orcfax feed integrator needs a more current update for a given Orcfax feed (e.g. ADA-FACT) than is available on-chain or through an existing heartbeat publication schedule, then an integrator can request its publication
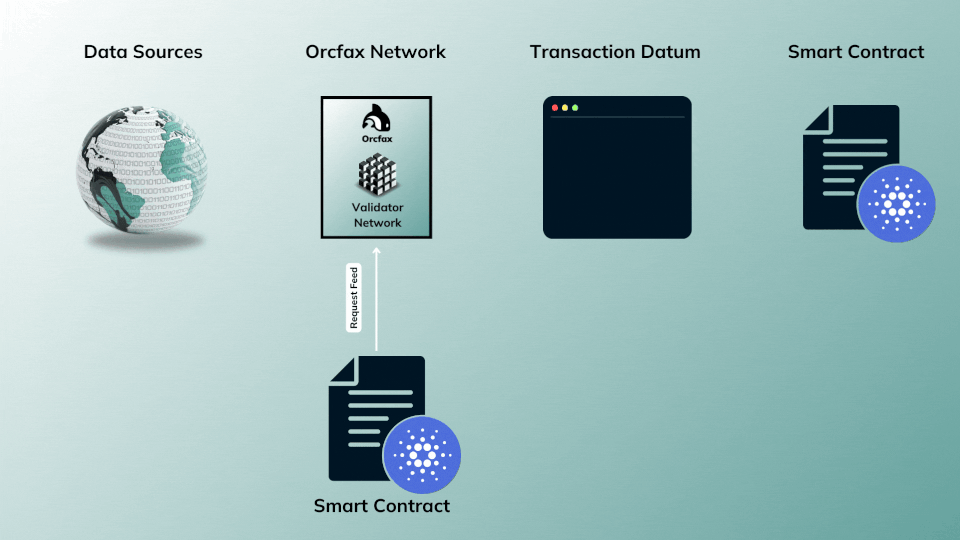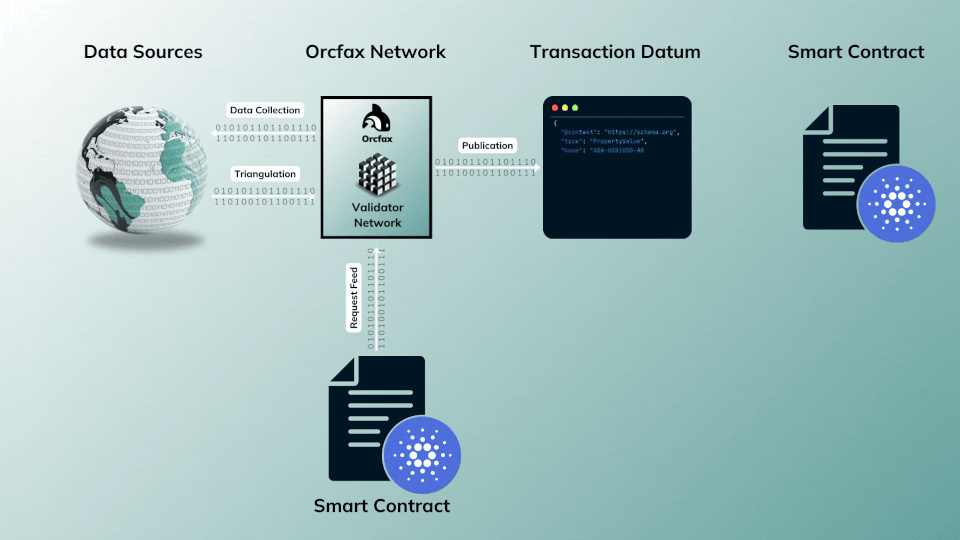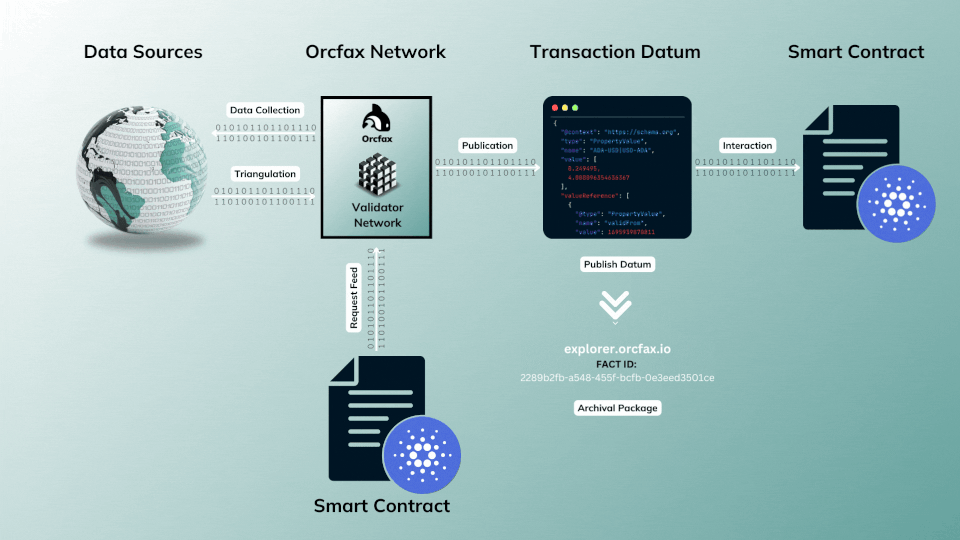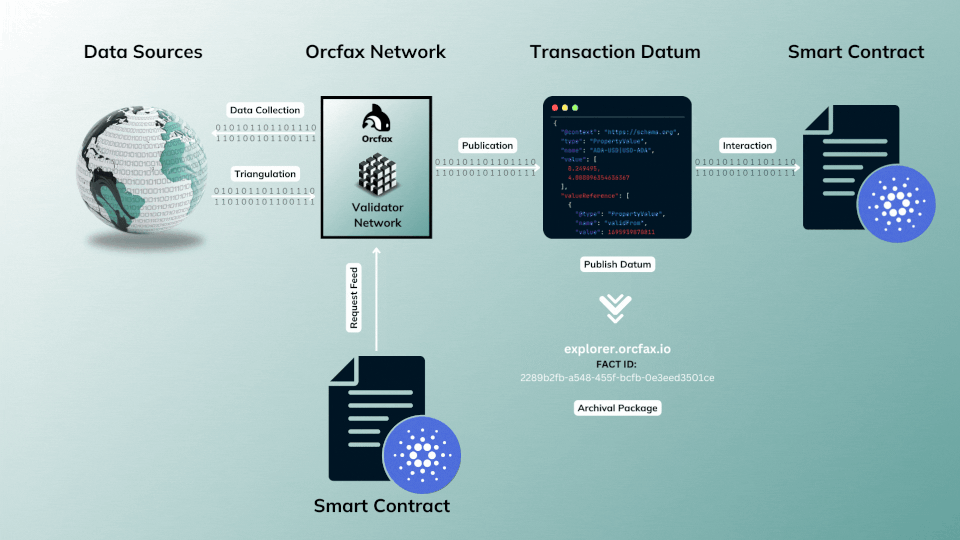
This publication model is often referred to as a pull based oracle, as the oracle service is directly triggered by requests made through a smart contract.
The benefits of the on-demand publication model is that integrators experience greater control over when data is made available. This service dramatically increases feed utility for dApps with use cases that can't justify a consistent heartbeat. Instead, the on demand publication model allows their smart contracts, and/or users to trigger Orcfax publication workflows for the data they need, when they need it.