The Orcfax vision
Oracles are a critical piece of blockchain infrastructure that when overlooked, or under-utilized, can have severe impacts on DeFi protocols.
An Oracle's primary role is to provide data about the real world, which the blockchain is ignorant of. When oracles bring this data on chain, it opens up a world of new possibilities for protocols which can utilize the data to underpin business logic and to serve as inputs to trigger smart contract execution.
However, the heavy reliance on oracles to provide these inputs, and the trust that consuming dApps must have in the data being utilized, creates new risk vectors: the risk of oracles being compromised, and the risk that oracles will feed blockchain smart contracts with false or inaccurate information; this is part of the "oracle problem".
The Cardano blockchain is a permissionless, public network, and while this fact greatly benefits users and developers, it also means that anyone can develop software or services for the purpose of providing smart contracts with data, all while claiming to fulfill the role of an oracle. We at Orcfax strongly object to this position.
The ability for software to be recognized as an "oracle" is reserved for those which have been intentionally designed to solve the "oracle problem", and DeFi protocols should look critically at any which do not explicitly address this issue.
The Oracle problem represents several interconnected issues regarding trust; Orcfax believes that solving the oracle problem means designing a solution from the bottom up with a focus on addressing decentralization and auditability.
Recent claims within the Cardano community of newly launched oracle solutions mean that users, now more than ever, need to assess the services being offered, the logic behind their design, how they are executed, and the implications of their use.
What follows is a short introduction to what Orcfax has identified as critical aspects of an oracle. It is our belief that solutions should be able to demonstrate these aspects in order to claim that their solution is in fact an oracle, and that it's addressing the "oracle problem" through the its provided service.
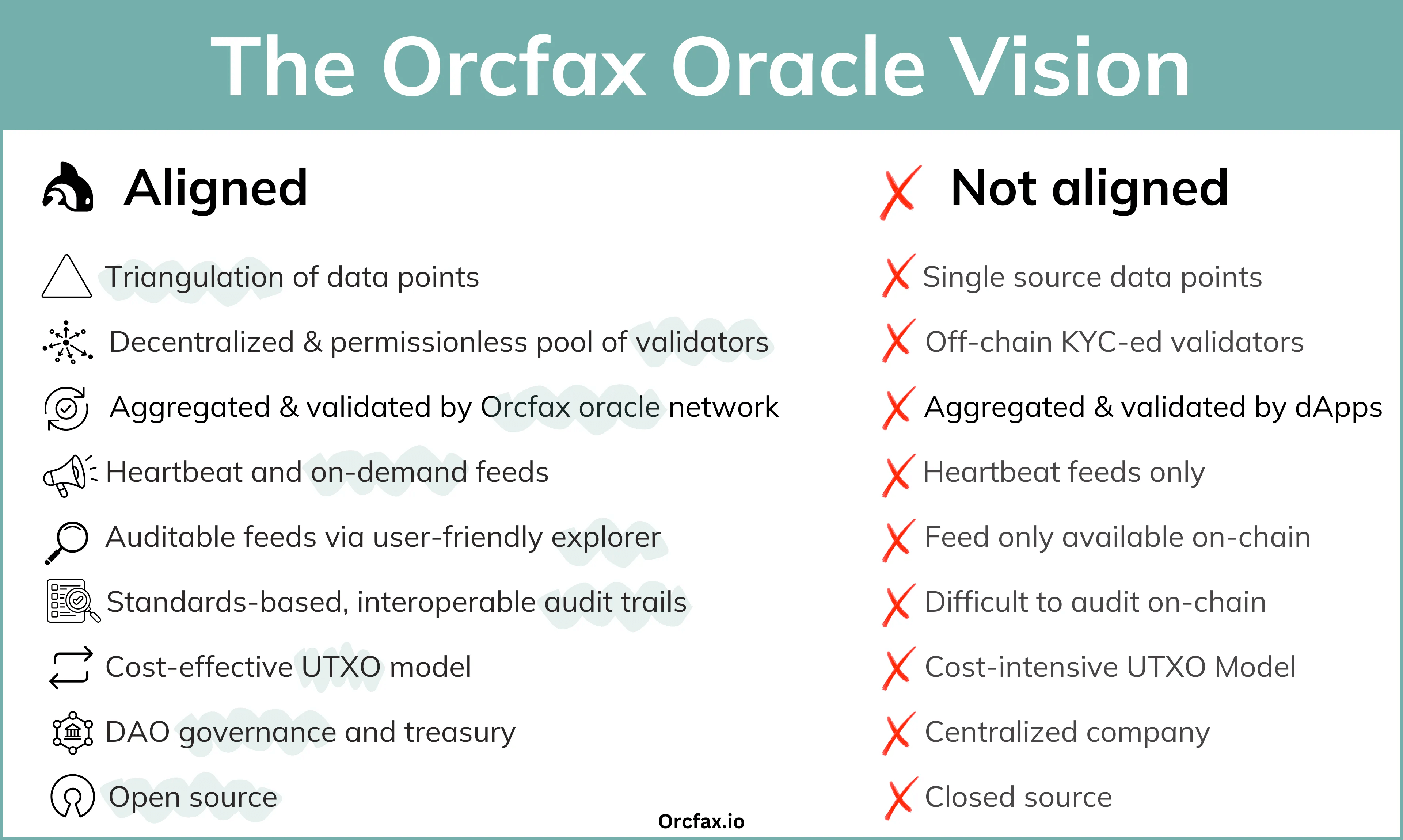
Breaking it down
The critical aspects of an oracle solution outlined in the above table demonstrate the Orcfax vision for Cardano oracles and how they should be designed in order to effectively address the oracle problem. To add more context, and to help users further appreciate how important these are, we unpack each of the above aspects, their significance, and how the Orcfax solution provides an answer.
Triangulation of data points vs Single source data points
To avoid single points of failure or attack, Orcfax has adopted the principle of triangulation, which is concerned with the utilization of multiple methods, or sources of information, in order to derive a comprehensive understanding of phenomena in the world; this principle also aids in testing the validity of source information by providing the ability to compare data across sources. In practice, the principle of triangulation is leveraged by our project to develop robust Orcfax nodes. Each of these nodes are required to query a min of 3 primary sources as a validation check. If one source fails, gets hacked, or contributes outlier data, then the remaining reliable sources can still be utilized to derive authentic values.
Orcfax released its first price feed (ADA-USD) with three primary sources being leveraged in accordance with this principle; however, updates to this feed and additional products benefit from an increased pool of primary source data providers, which enhances their reliability and security.
Decentralized & permissionless pool of validators vs Off-chain kyc-ed validators
Requiring data validators to go through regulatory know-your-customer (KYC) processes and/or requiring individuals to sign contracts goes against the very decentralization ethos that Orcfax is championing. Truly decentralized networks are permissionless; this means that the only limiting factor for network participants should be their ability to meet the minimal technical requirement identified for node operation.
It is our belief that those sympathetic to the goals of decentralization should strongly object to oracle solutions that require users to rely on trusted third party companies to act as gatekeepers for, what should be, a community resource.
Aggregated & validated by Orcfax vs Aggregated and validated by dApp
The oracle problem represents significant risks for dApps and has implications for the data that their smart contracts rely upon in order to execute transactions. However, dApps can, and should, reduce their risk significantly by integrating oracle feeds and leveraging input data that comes from a decentralized validator pool, run by independent operators.
Several solutions across Cardano have developed their own in-house, and often ad hoc, oracle solutions in order to meet the data needs of their smart contracts. Whether this has been for lack of an alternative solution or incompatibility with solution providers on offer, dApps inject significant risk into their protocols by relying on oracle solutions which have not been diligently researched and purpose built.
Orcfax can help dApps focus on their core services by doing the data gathering, aggregation, and validation work, which would otherwise unnecessarily slow down smart contract execution, increase transaction costs, and introduce new attack vectors for their dApps.
It can't be stressed enough, when dApps and protocols only use their own in house data solutions, or do their own external data gathering, they create serious attack vectors. Choosing not to leverage purpose built solutions can also result in justifiable mistrust amongst the users of their DeFi products, as it is often their assets which are put at risk by these design decisions.
Heartbeat & on-demand feeds vs Heartbeat feeds only
The number of potential use cases for oracle feeds are numerous, and they are increasing every day as developers create exciting new products, and as blockchains position themselves for increased adoption. While there can be overlap in the data needs of dApps and their smart contracts, many of these use cases have their own distinct requirements in regards to when data must be available on chain.
Orcfax recognizes these differences and the unique needs of integrators. Because of this, we have developed services to suit and accommodate dApp requirements. Our solution will now support two distinct publication models: heartbeat and on-demand.
Our ADA-USD feed went live on mainnet by leveraging the first of these publication options– an Orcfax hourly heartbeat publication model with deviation monitoring.
The heartbeat publication model gives integrators the ability to access data at regular intervals which can be set according to their needs (e.g. once per hour). More about this publication model can be found in the heartbeat publication model
The on-demand publication model allows complete flexibility and gives dApps even more control of data use by allowing them to request data collection, validation and publication whenever it's needed by their smart contracts. More about this publication model can be found in the on-demand publication model
Auditable feeds via user friendly explorer vs Difficult to audit on-chain
When something goes wrong with software, every user, including non-developers, should be able to audit all aspects of the processes involved— blockchain oracles are no different. Users must have the ability to follow detailed documentation that recounts the processes, their outputs, and how the steps taken resulted in the oracle values published on-chain and utilized by smart contracts.
Not only should this documentation exist in a way that is easy to access, the information needs to be intelligible for users of diverse skill sets and to future audiences that may lack context.
Orcfax has addressed both of these requirements by creating human and machine-readable audit trails of all Orcfax solution processes: data collection, normalization, aggregation, validation, and publication. This is made possible by leveraging standards-compliant record-keeping practices that ensure the links between all the on-chain and off-chain components are immutable, inextricable, and trustworthy.
While these records can be interrogated manually, we have developed a user-friendly Explorer interface that makes surfacing these audit trails simple and convenient so that users of Orcfax feeds can "Trust But Verify". The explorer was developed as a direct response to the disregard that other solutions have shown regarding the right of users to conduct their own audits, the need to prioritize accessibility, and ease of use; unlike other oracle solutions, the Orcfax Explorer does not require expert knowledge of Cardano eUTXO architecture, nor does it force users to execute complicated forensic processes to follow on-chain transactions. Everything users need is made available at their finger tips.
Standards-based interoperable audit trails vs Feed only available on-chain
This point complements the previous by focusing on the value of re-use; Orcfax strongly believes that there is significant secondary value for real-world data that has gone through vigorous authenticity and accuracy checks, like the information that Orcfax publishes to the Cardano blockchain. Therefore, our audit trail packages are marked up using a number of key industry standards including JSON-LD, Schema.org, and IETF Bagit.
The archival packages are designed to preserve on-chain data, and their context, all while using identifiers which link all associated records and creates a permanent link back to the on-chain Cardano transactions containing the relevant Orcfax datum. The result is that Orcfax provides blockchain-based trust anchors for Fact Statements about the real world that are now highly interoperable and re-usable beyond Web3 (e.g. training AI models on validated real-world Facts).
Orcfax is committed to continuing its R&D into new ways to reuse feed data and to leverage this "data lake of validated facts" for new value-added services and products.
Cost-effective UTXO model vs Cost-intensive UTXO model
Cardano was designed to off-load as much transaction processing as possible to off-chain components in order to minimize on-chain computations and thereby dramatically reduce transaction costs. The Cardano blockchain has been able to accomplish this without significant security compromises. The Orcfax oracle architecture has been intentionally designed to follow the same design and delegation principles.
Orcfax has managed to reduce on-chain interaction to a single certified data publication event, all while providing linkages that connect on-chain datapoints with a complete history of supporting documentation related to all off-chain processes; these records are made available permissionlessly through decentralized storage, and have standards-based security guarantees for their links back to the on-chain data.
Other oracle solutions require users to juggle the handling of numerous NFTs and a complicated series of inter-dependent on-chain transactions to support their workflow, each adding transaction fees along the way. These other solutions are neither efficient nor cost effective for their integrators and end users.
Orcfax has designed its solution with a commitment to minimal transaction fees for integrators, making it the most cost-effective and long-term sustainable oracle solution on Cardano. And R&D continues as Orcfax continues to find strategies to optimize feed publication and to maximize integrator ease of use.
DAO governance & treasury vs Centralized company
While the Orcfax project was initially established through its incorporation as a company in the British Virgin Islands, and has continued to leverage this position for development, this was always meant to be temporary. The sole purpose of the Orcfax Ltd. company is to develop, and launch, the Orcfax Network while also performing custodial duties for the FACT token.
It is our desire that as soon as specific implementation targets are reached, Orcfax Ltd. will dissolve itself and initiate the transfer of Orcfax Network operations to the Orcfax Foundation, which will be operated as a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO).
The Orcfax commitment to DAO governance was enshrined in our tokenomics wherein 5% of the total $FACT supply was reserved, within its own distinct ada handle, for the sole purpose of funding the operations of the Orcfax Foundation. After Orcfax Ltd. has delivered the full roadmap and has dissolved itself, the DAO will become the recipient of the network share of $FACT data feed fees.
We envision that the DAO will be run via stake-based voting using $FACT to decide on housekeeping matters, hiring contractors to monitor daily network operations, hiring developers to add new features, to make decisions on network parameters such as transaction fee percentages, and whether or not to add or remove certain feeds.
Importantly, current Orcfax activities and development have been largely funded via our successful FACT token launch. Many other oracle providers have been funded by venture capitalists (VCs) who are averse to any type of DAO/community based governance that affects their ability to get a return on their investment (e.g. pull value out of the oracle project). We object to these kinds of project financing strategies as they effectively tie the project's hands and can prevent the development and fostering of decentralization; alignment with VCs also causes the project to be beholden to them, whereas we prefer to be beholden to our community.
Open-source vs Closed-source
The Orcfax team stalwartly believes in the open-source software ethos, which prioritizes equitable access by allowing users to copy, inspect, and alter software source code for the benefit of their own projects. Another key benefit is that this creates a unique auditing environment; the concept of, "more eyes on the code", demonstrates this phenomena and is meant to convey scenarios where it's more likely that developers outside the core team are able to spot, and willing to help fix, any bugs or errors in the software.
The Orcfax project itself leans heavily on other free and open-source software components, and stands on the shoulders of developers who have committed their work to the benefit of the public. Because of this, we recognize the responsibility of our project to pay it forward, and this will be done through the software which we open-source.
While we have already open-sourced a number of Orcfax projects, we will continue to do so as components enter production and maturity until we have incrementally open-sourced the Orcfax oracle solution.
What is the Orcfax difference?
We believe that the purposeful design of the Orcfax solution and the incorporation of the above critical aspects demonstrates how Orcfax sets itself apart from other oracle solution attempts in the Cardano space. With that said, Orcfax isn't finished; our team continues to research the oracle problem, to develop decentralized solutions, and continues to focus on providing data services which users can trust, but verify. This is the Orcfax difference, and and what separates our solution from the others.