Data collection
Decentralizing data collection
Since the roll out of our ADA-USD feed, Orcfax has committed to educating users on the critical importance of rejecting data derived from single sources and the necessity for source redundancy. Orcfax addresses both of these and avoids single points of failure or attack by leveraging the principle of triangulation, which is concerned with the utilization of multiple methods, or sources of information, in order to derive a comprehensive understanding of phenomena; this principle also aids in testing the validity of source information by providing the ability to compare the data across sources. This principle has been enshrined in Orcfax node development and made evident in the processes by which Orcfax nodes collect data.
Each Orcfax node is required to query, and receive data from, a minimum of 3 primary sources. This principle of triangulation protects the reliability and authenticity of oracle data. In practice, Orcfax node design uses the principle of triangulation in order to enable nodes to function even in scenarios where sources fail to return data, are compromised, or report anomalous data. In each of these scenarios, the principle means that nodes remain flexible and resilient given that they meet the threshold for minimum data sources which enables the network to maintain data integrity and reliability while being unaffected by outliers.
If nodes query 5 sources, but only receive inputs from 4, the nodes can still successfully triangulate the data as the received inputs still meet the 3 source minimum.
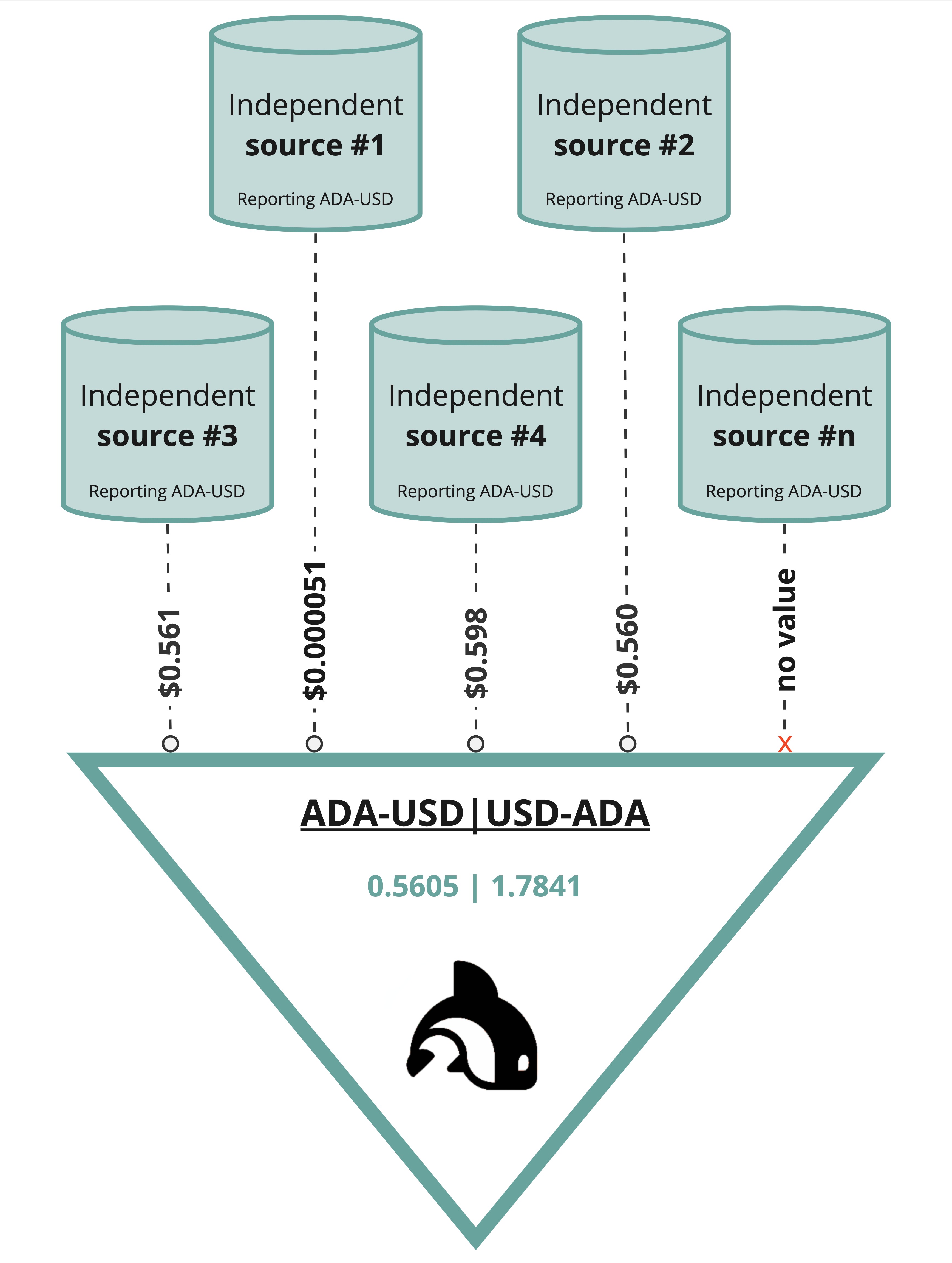
Our adherence to the principle of triangulation allows a more thorough response to the oracle problem by providing nodes the ability to compare data across multiple sources which allows them to assess the authenticity and accuracy of the data.
Leveraging decentralized data gathering on chain
The same data collection principles and standards used in Orcfax price feeds are also leveraged in Cardano Native token (CNT) feeds. Orcfax has chosen to leverage DEX Liquidity pools in order to report token pair values. This is because liquidity pools provide a unique and efficient price discovery mechanism. Within the pool, a token pair derives comparative value according to a simple mathematical formula that calculates price, in real time, as users affect the token-to-token ratio by adding or removing from either side of the currency pair. Because of this innate price discovery mechanism in liquidity pools, Orcfax has the ability to provide a simple and elegant solution for decentralized CNT feeds.
Regardless of the CNT feed requested by integrators, Orcfax will leverage its network of validator nodes to execute the collection process. Each node will be responsible for querying the cardano ledger, in order to collect the total liquidity per token pair on each DEX. These liquidity values are then calculated through virtual liquidity pooling to derive an aggregated liquidity pool for that token pair.
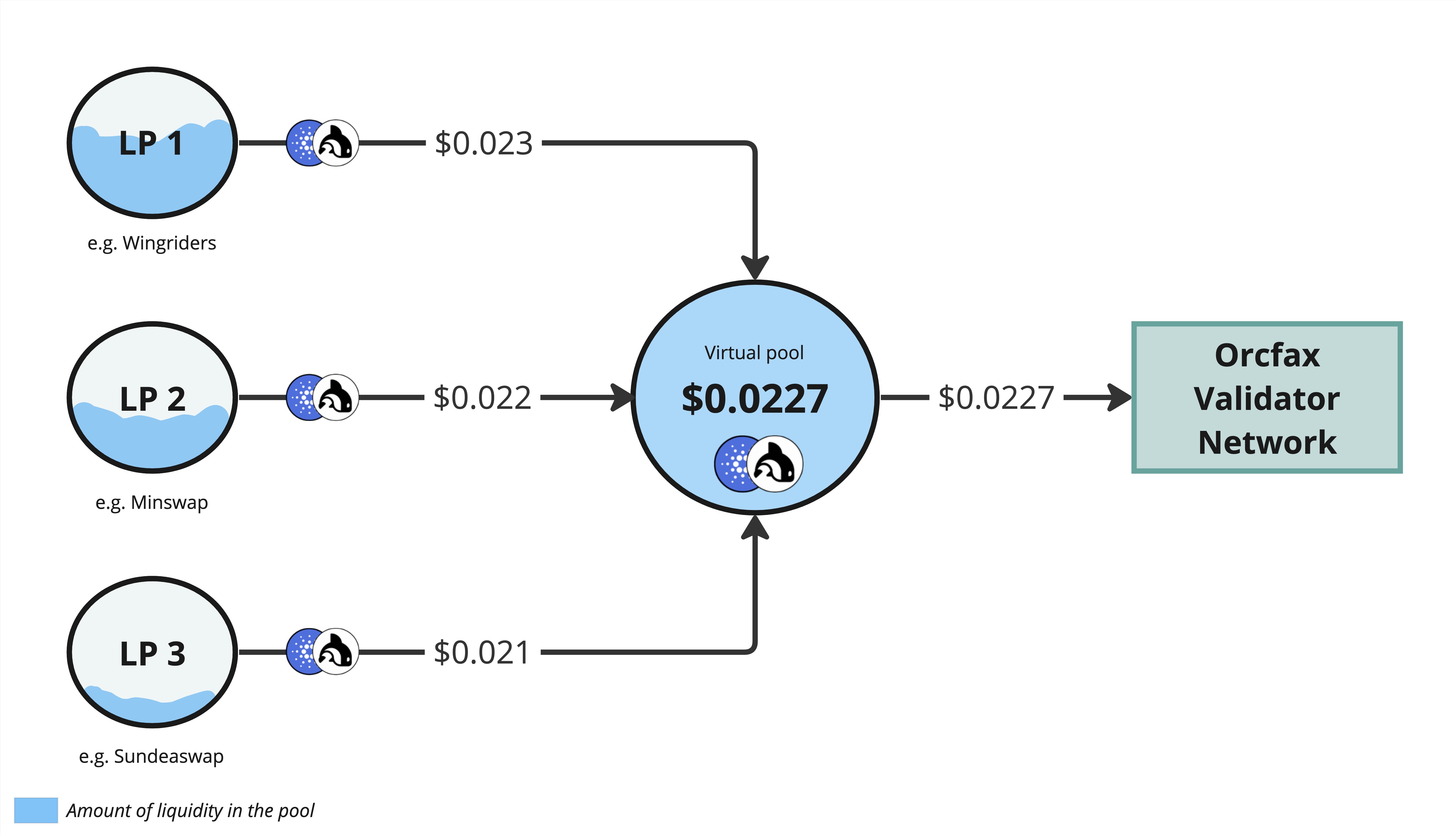
The virtual liquidity pool will then reflect the aggregated price of that token pair, as observed by that specific node. This approach removes the risk of low liquidity DEXes skewing the price to allow manipulation.
Each Orcfax node will perform the same process and share their derived values with the rest of the validator network in order to normalize, validate and finally publish on the Cardano blockchain. This data can then be used as trustworthy reference inputs to trigger different kinds of business logic in Cardano smart contracts and dApps.